Topics : GS-3, Environment, Biodiversity conservation, UPSC Prelims
References https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/fifty-years-of-project-tiger-how-the-programme-saved-indian-tigers-8547213/ https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-illegal-mining-in-sariska-9339325/
https://ntca.gov.in/tiger-reserves/#tiger-reserves-2
India’s Tiger Conservation Plan
India, home to the majestic Bengal Tiger, takes pride in its efforts to conserve this national treasure. The Wildlife Protection Act of 1972 serves as the foundation for the conservation of the tiger and their habitat.
Creating Safe Havens: Tiger Reserves
India’s Tiger Conservation Plan (TCP) facilitates the creation of these sanctuaries, called Tiger Reserves. A tiger reserve is a protected area in India where tigers and other wildlife are preserved and conserved. These reserves are established to ensure the survival of tigers and their habitat, and to promote biodiversity, tourism and sustainable development.
Creation of Tiger Reserves
- State Takes Charge: The authority to designate these reserves lies with the state governments.
- Expert Guidance: Following the recommendations of the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA), these crucial areas are officially notified for protection under Section 38V of the Wildlife Protection Act.
Goals for a Thriving Ecosystem:
The TCP goes beyond just establishing reserves. It outlines a multi-pronged approach to ensure a healthy tiger population and a flourishing ecosystem.
- Protecting the Tiger’s Domain: Habitat protection and management are top priorities. This includes safeguarding the reserves themselves and implementing practices that enhance the habitat for tigers, their prey, and other predators that share their environment.
- Connecting the Dots: Ensuring tigers can find mates and disperse to new territories is essential. The TCP promotes land-use practices within and surrounding the reserves that are ecologically sound. This creates corridors, like natural bridges, between protected areas, allowing tigers safe passage.
- Sustainable Forestry: The plan extends its focus beyond the protected zones. It addresses forestry practices in nearby regular forests, ensuring they are conducted responsibly and don’t negatively impact the delicate balance within the tiger reserves.
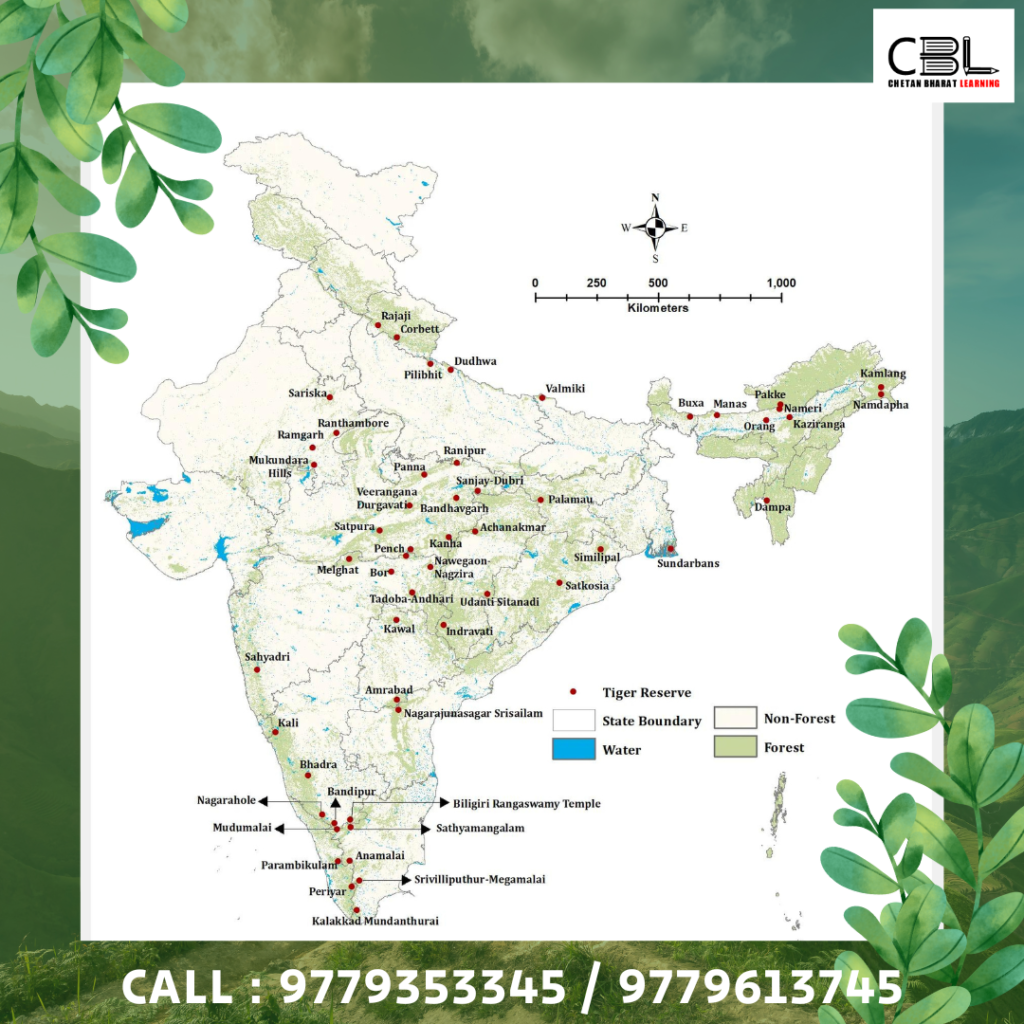
Tiger Reserves and Other Conservation areas in News
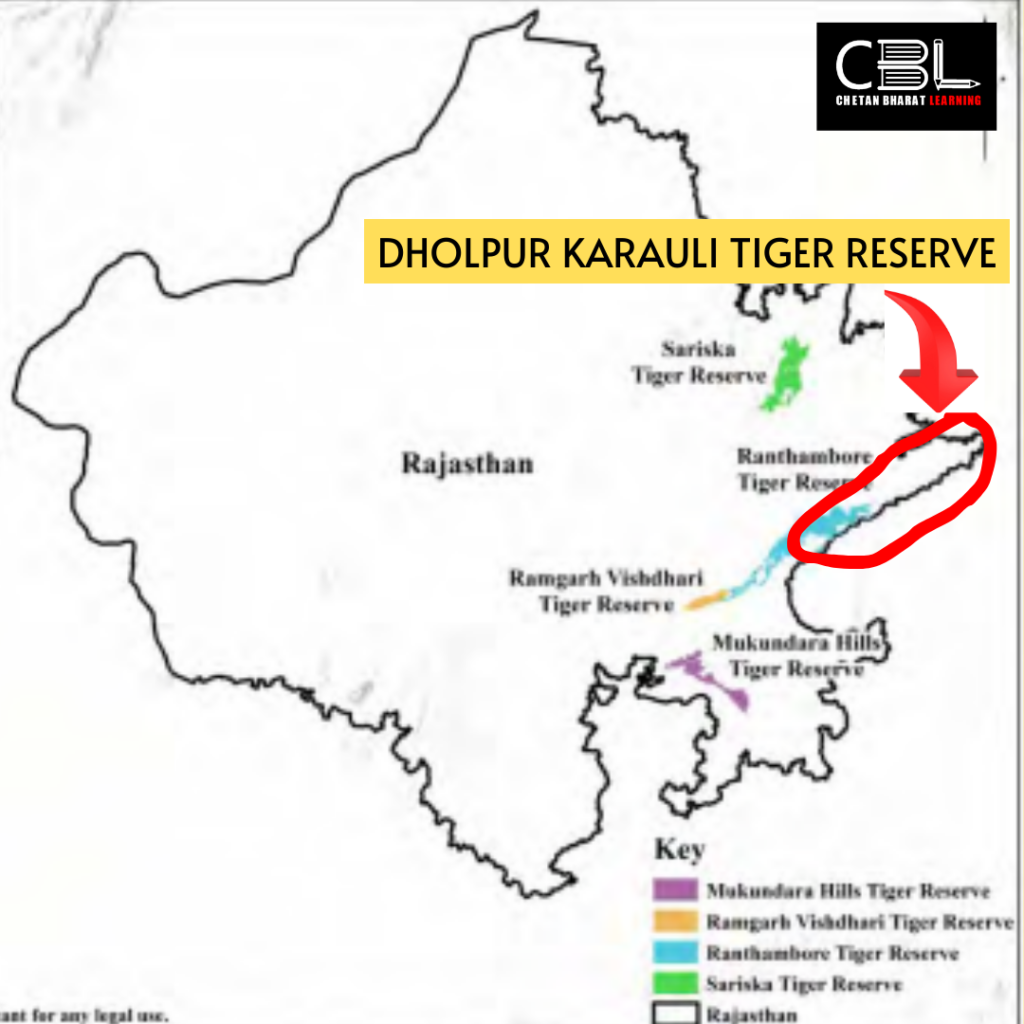
- Dholpur – Karauli Tiger Reserve in Rajasthan: The National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) gave the green light to Rajasthan’s fifth tiger reserve – the Dholpur-Karauli Tiger Reserve. Spanning an area of 1075 sq km, the reserve boasts two distinct zones: a core area of 580 sq km offering prime tiger habitat and a buffer zone of 495 sq km. The reserve’s location flanks existing protected areas like Ranthambore, Ramgarh Vishdhari, and Mukundra Hills, creating a vital wildlife corridor that bridges Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh.
- Veerangana Durgavati Tiger Reserve in Madhya Pradesh
- Ranipur Tiger Reserve in Uttar Pradesh
- Ramgarh Vishdhari Tiger Reserve in Rajasthan
- Srivilliputhur Megamalai Tiger Reserve in Tamil Nadu
- Kamlang Tiger Reserve in Arunachal Pradesh (Lohit District)
- Orang Tiger Reserve in Assam
- Palamau Tiger Reserve in Madhya Pradesh
- Dampa Tiger Reserve in Mizoram
- Simlipal Tiger Reserve in Odisha
- Kalakad Mundanthurai Tiger Reserve in Tamil Nadu
- Anamalai Tiger Reserve in Tamil Nadu
- Dudhwa National Park in Uttar Pradesh
- Kumbhalgarh Wildlife Sanctuary in Rajasthan
- Sariska Tiger Reserve in Rajasthan
- Amrabad Tiger Reserve in Telangana
- Melghat Tiger Reserve in Maharashtra


Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.