What is El Nino?
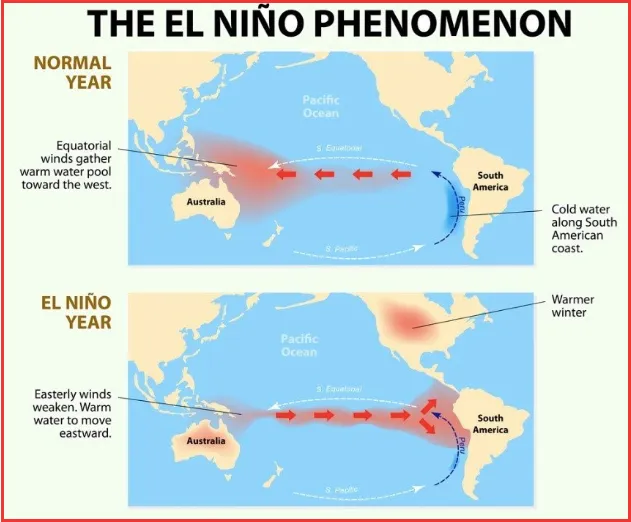
El Nino is a complex climate phenomenon characterised by the abnormal warming of Sea Surface Temperature (SST) in the Eastern Pacific Ocean.
- Often known as the warmer phase of El – Nino Southern Oscillation, it typically occurs every two to seven years and can last for several months to over a year.
- Peruvian fishermen were the first to notice the occurrence of unusually warm water off the coast of Peru in the 1600s. Spanish immigrants termed it “El Niño,” which translates to “little boy” in Spanish.
- Over time, El Niño came to represent the warming of coastal waters, irregular and intense climate fluctuations.
- El Niño events are not regular occurrences; they are unpredictable and happen irregularly.
- Climatologists have observed that El Niño coincides with the Southern Oscillation. The Southern Oscillation is a change in air pressure over the tropical Pacific Ocean. When the eastern tropical Pacific’s coastal waters warm up (El Niño), the atmospheric pressure above the ocean decreases.
- Climatologists have coined the term El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) to describe these interconnected phenomena of El-Nino and La-Nina.
ENSO
Under normal conditions, the tropical south Pacific ocean witnesses high pressure whereas the tropical Indian Ocean undergoes low pressure conditions. Sometimes, these pressure conditions are reversed, resulting in low pressure in the Pacific and high pressure in the Indian Ocean.This is the periodic change in pressure conditions which is referred to as the Southern Oscillation. The phenomena of changing pressure conditions in both the oceans is connected to El Nina and is referred to as the El Nino Southern Oscillations or the ENSO.
Causes of El-Nino
- Warm water accumulates in the eastern Pacific near the equator. The accumulation disrupts the normal ocean-atmosphere interactions in the region leading to changes in atmospheric circulation patterns, including the weakening of the trade winds and the weakening of the typical low-pressure system in the western Pacific.
- As a result, warm surface waters migrate eastward towards South America, suppressing the normal upwelling of cold, nutrient-rich water along the coasts of Peru and Ecuador.
- This disruption of the normal oceanic circulation patterns leads to the characteristic warming of sea surface temperatures in the eastern Pacific, which in turn influences global weather patterns.
- The warming of sea surface temperatures in the eastern Pacific affects the distribution of atmospheric pressure and temperature gradients, leading to changes in atmospheric circulation patterns and the formation of rainstorms in certain regions. These changes in weather patterns can have far-reaching impacts on climate, ecosystems, and human societies around the world.
El Nino Monitoring
A number of technologies such as scientific buoys are used by scientists, governments, and non-governmental organisations (NGOs) to collect data about El Nino.
- A buoy is a type of an object that floats in water and is used in the middle of the seas as locators or as warning points for the ships. They are generally bright (fluorescent) in colour.
- Used to measure ocean and air temperatures, currents, winds, and humidity.
- The scientists can more accurately predict El Nino and visualise its development and impact around the globe with the help of data transmitted by the buoys daily to researchers and forecasters around the world.
- The Oceanic Nino Index (ONI) is used to measure deviations from normal sea surface temperatures.
Impact of El- Nino
- Temperature Anomalies: El Niño typically brings warmer-than-average sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern Pacific Ocean. This can lead to higher air temperatures in many regions, affecting weather patterns and ecosystems.
- Altered Precipitation Patterns: El Niño can disrupt normal precipitation patterns, causing droughts in some areas and increased rainfall in others. For example, it often brings heavy rains to the western coast of South America and drier conditions to Southeast Asia and Australia.
- Hurricane Activity: El Niño tends to suppress Atlantic hurricane activity while enhancing it in the eastern Pacific. The warmer ocean temperatures associated with El Niño can fuel the development of tropical storms and hurricanes, impacting coastal communities and economies.
- Agricultural Impacts: The altered precipitation patterns and temperature anomalies associated with El Niño can have significant effects on agriculture. Droughts can lead to crop failures and food shortages, while excessive rainfall in others can cause flooding and damage to crops.
- Fisheries: El Niño can disrupt marine ecosystems, affecting fish populations and fisheries. It can lead to changes in ocean currents and water temperatures, impacting the distribution and abundance of fish species.
Impact of El- Nino in India
- Monsoon Patterns: El Niño typically leads to weakening of the Indian summer monsoon. Summer Monsoon brings the majority of the country’s annual rainfall. This weakening can result in below-average rainfall in many parts of India, leading to drought conditions and water shortages.
- Agriculture: Reduced monsoon rainfall during El Niño years can have significant impacts on agriculture. Crop yields may decline due to water stress, leading to lower production of food crops such as rice, wheat, and pulses. This can affect food security and livelihoods for millions of people, particularly in rural areas.
- Water Resources: Drought conditions can lead to depletion of water resources, including rivers, reservoirs, and groundwater aquifers.
- Heatwaves: El Niño can contribute to above-average temperatures in many parts of India, exacerbating heatwave conditions. High temperatures have adverse effects on human health, increasing the risk of heat-related illnesses and mortality, especially among vulnerable populations.
- Economic Impacts: The agricultural sector is a significant contributor to India’s economy. Fluctuations in crop yields due to El Niño can have economic repercussions. Lower agricultural output can affect food prices, trade balances, and rural incomes, influencing overall economic growth and development.
- Health Risks: El Niño-induced droughts and heatwaves can increase health risks for the population. Water scarcity and poor sanitation during droughts can contribute to the spread of waterborne diseases. Heat waves can lead to heat exhaustion, heatstroke, and other heat-related illnesses.


Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.