
Important for UPSC, State PCS
Prelims: ASEAN , SINGAPOR , Act East Policy , Free Trade Agreement , South China Sea , SAGAR .
Mains: General Studies Paper 2 – Significance of ASEAN for India, Key Concerns in India-ASEAN Relations.
ASSOCIATION OF SOUTHEAST ASIAN NATION (ASEAN)
ASEAN History
- The Association of Southeast Asian Nations, or ASEAN, was established on 8 August 1967 in Bangkok, Thailand, with the signing of the ASEAN Declaration (Bangkok Declaration) by the Founding Fathers of
- The motto of Association of Southeast Asian Nations is “One Vision, One Identity, One Community”.
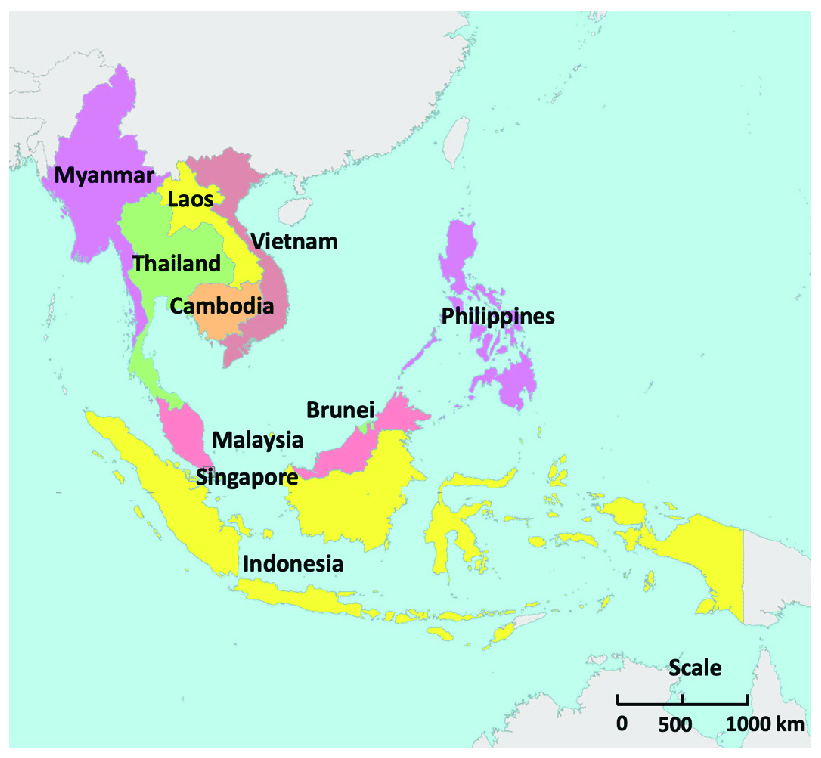
ASEAN Member Countries
Association of Southeast Asian Nations Secretariat – Indonesia, Jakarta
Founding Members Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore and Thailand.
Brunei Darussalam (1984), Vietnam (1995), Lao PDR and Myanmar (1997), and Cambodia (1999), joined the ASEAN later.
Evolution of ASEAN
- 1967 – ASEAN was established with the signing of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations Declaration (Bangkok Declaration) by its founding fathers.
- 1990s – Membership doubled after the changing conditions in the region following the end of the Vietnam War in 1975 and the Cold War in 1991. Addition of Brunei (1984), Vietnam (1995), Laos and Myanmar (1997), and Cambodia (1999).
- 1995 – Members signed a deal to create a nuclear-free zone in Southeast Asia.
- 1997 – Adoption of Association of Southeast Asian Nations Vision 2020.
- 2003 – Bali Concord II for the establishment of an ASEAN Community.
- 2007 – Cebu Declaration, to accelerate the establishment of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations Community by 2015.
- 2008 – Association of Southeast Asian Nations Charter comes into force and becomes a legally binding agreement.
- 2015 – Launch of Association of Southeast Asian Nations Community.
Institutional mechanism of ASEAN
The institutional mechanism of ASEAN include
- ASEAN Summit: It meets annually to discuss regional issues and set policy directions.
- ASEAN Coordinating Council (ACC): It oversees the implementation of ASEAN agreements and decisions.
- ASEAN Secretariat: It supports and facilitates ASEAN’s activities and initiatives.
- ASEAN Regional Forum (ARF): It is a platform for dialogue and cooperation on political and security issues among ASEAN member countries and their partners.
- Decision Making: It is done through consultation and consensus.
the history of India-ASEAN countries relations ?
Initial Years of engagement–
India-ASEAN countries formal engagement began in 1992 as a ‘Sectoral Dialogue Partner‘ (Secretary level interaction). The partnership was instituted as a ‘Dialogue Partner‘ in 1995, which entailed interaction at the Foreign Minister’s level. The partnership was elevated to the summit level in 2002.
Era of Strategic Partnership–
At the commemorative Summit meeting celebrating 20 year relationship between India and ASEAN, the partnership was elevated to a strategic partnership. During the 25-year Commemorative Summit in New Delhi (January 2018), India and ASEAN agreed that our Strategic Partnership will be focused on building cooperation in the maritime domain.
Comprehensive Strategic Partnership –
The year 2022 marks the 30 years of ASEAN-India relations, and the year has been designated as the year of India-ASEAN countries friendship. At the 19th ASEAN-India Summit to commemorate 30th anniversary of ASEAN-India Dialogue Relations, the Strategic Partnership was elevated to the Comprehensive Strategic Partnership. On this occasion, ‘Joint Statement on ASEAN-India Comprehensive Strategic Partnership‘ was released
Economic Cooperation–
- ASEAN is India’s fourth largest trading partner.
- India’s trade with the Association of Southeast Asian Nations stands at approx. 6% of India’s overall trade.
- India’s export to the Association of Southeast Asian Nations stands at 28% of our total exports. The ASEAN-India Free Trade Area has been completed.
- Association of Southeast Asian Nations India-Business Council (AIBC) was set up in 2003 to bring key private sector players from India and the ASEAN countries on a single platform.
- Major exports from India to the region: Ships, boats, floating structures, mineral fuels, mineral oils and meat.
- Major imports: telecom equipment, electrical machinery, mineral fuels, mineral oils and animal or vegetable fats and oils.
Association of Southeast Asian Nations-India Green Fund
Socio-Cultural Cooperation: Programmes to boost People-to-People Interaction with Association of Southeast Asian Nations, such as inviting ASEAN students to India, Special Training Course for ASEAN diplomats, Exchange of Parliamentarians, etc.
Funds: Financial assistance has been provided to ASEAN countries from the following Funds:
Association of Southeast Asian Nations-India Cooperation Fund
Association of Southeast Asian Nations-India S&T Development Fund
What opportunities does ASEAN provide for India ?
ASEAN is significant for India in several ways:
Important for rule-based order: ASEAN plays a central role in promoting a rules-based security architecture in the Indo-Pacific region, which is essential for the region’s stability and prosperity.
Potential market: ASEAN constitutes the 3rd largest market in the world. This can help India utilize its export potential.
Convergence with Indo-Pacific strategy: ASEAN is a crucial component of India’s “Act East” policy and its “Indo-Pacific” strategy, reflecting the convergence of interests in the region.
Countering China’s influence: Strengthening relations with ASEAN countries can serve as a counterbalance to China’s influence in the region.
Connectivity with North East: Connectivity initiatives with ASEAN can boost economic development in India’s northeastern states by positioning them as a hub for regional trade and commerce.
What should be the way forward to improve India-ASEAN relations?
Some of the steps that can be taken to improve India-ASEAN relations include:
- Enlarging QUAD: The concept of QUAD can be expanded to include the ASEAN countries and become a QUAD+ arrangement.
- Maritime Security in the Indo-Pacific: ASEAN countries have limited military ties with China due to maritime disputes. India can fill this gap and become a significant military partner in the region.
- Strengthening cultural connect: Tourism can be further encouraged between India and the ASEAN with some creative branding by the two sides.
- Strengthen connectivity: Strengthening land, air, and sea linkages will enhance people-to-people flows, as well as boost business, investment, and tourism.
Collaborating in International and Regional forums: India and ASEAN countries can work together to promote their common interests in international and regional forums such as the United Nations, East Asia Summit, and ASEAN Regional Forum
CBL Practice Questions for Prelims –
Which initiative is aimed at enhancing connectivity between India and ASEAN?
a) Act East Policy
b) South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC)
c) North East Vision 2020
d) G20 Summit
Answer: a) Act East Policy
CBL Mains Practice Question –
Discuss the significance of the Act East Policy in enhancing India-ASEAN relations. What challenges does India face in implementing this policy ?




Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.