What is La Nina?
La Nina is a climate phenomenon characterised by cooler-than-average sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern Pacific Ocean near the equator, which can have significant impacts on weather patterns around the world.
- It is essentially the counterpart to El Nino, which is marked by warmer-than-average sea surface temperatures in the same region.
- La Nina events bear witness to an increase in rainfall in the western Pacific and Southeast Asia, leading to wetter-than-normal conditions in those areas. Conversely, regions like the western coast of South America often experience drier conditions.
- La Nina can also influence weather patterns in North America, bringing colder and wetter conditions to the northern part of the continent, while the southern United States may experience warmer and drier conditions.
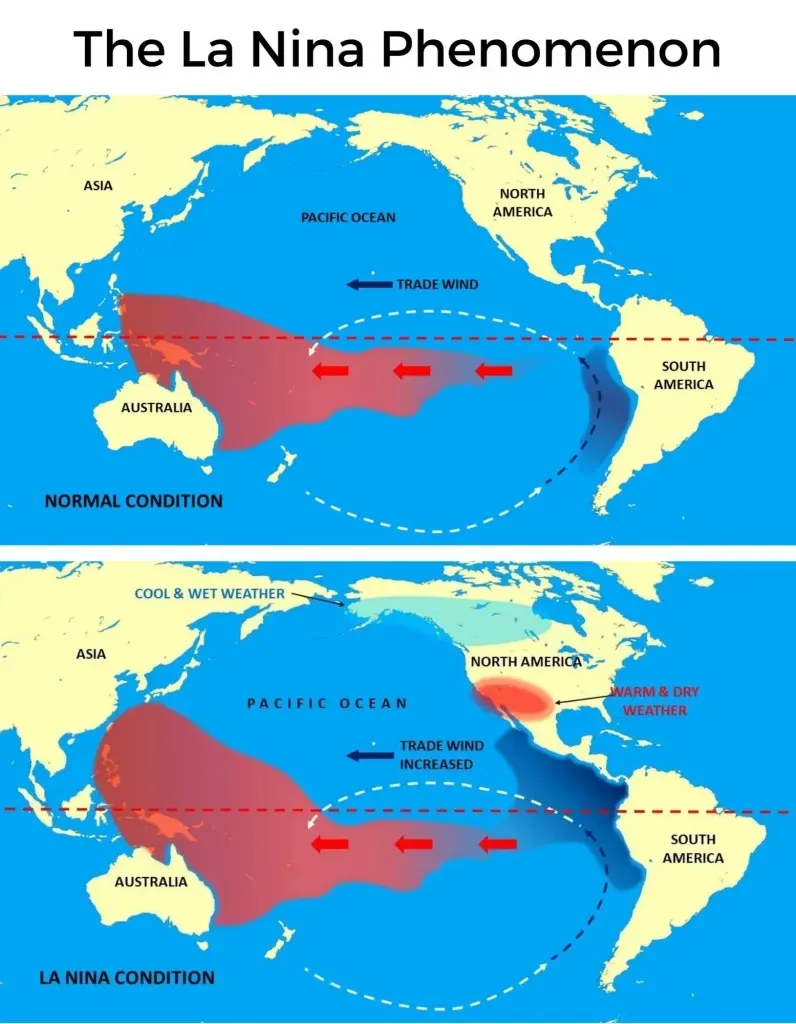
LA NINA triggers the following events:
- Ecuador and Peru witness droughts.
- Heavy floods in Australia.
- High temperatures in the Indian Ocean, Western Pacific, and off the coast of Somalia.
- Good monsoon rains are experienced in India. La Nina years are better than normal monsoons in India.
- Thus beneficial for Indian Monsoons.
Global Impacts
- Weather Patterns:It brings about distinct weather patterns globally, including increased rainfall in the western Pacific and drier conditions in parts of Australia and Indonesia. Conversely, it can lead to wetter conditions in the southern United States and parts of South America.
- Hurricane Activity: It tends to enhance hurricane activity in the Atlantic basin, increasing the likelihood of more frequent and intense hurricanes. This can have significant implications for coastal communities, leading to heightened risks of damage and loss of life.
- Temperature Anomalies: Regions experiencing La Nina often witness temperature anomalies. For instance, parts of the northern United States and Canada may experience colder-than-average temperatures during the winter months, while areas such as the southern United States may experience warmer-than-average conditions.
- Agricultural Impacts: It can have both positive and negative effects on agriculture, depending on the region. Increased rainfall in some areas may benefit crops, leading to higher yields. However, drought conditions in other regions can adversely affect agricultural productivity, leading to crop failures and food shortages.
- Fisheries: La Nina can disrupt marine ecosystems, impacting fish migration patterns and the availability of certain species. This can affect both commercial and subsistence fisheries, potentially leading to economic losses for communities dependent on fishing.
- Water Resources: The distribution of precipitation associated with La Nina can affect water resources and availability. While some regions may experience increased rainfall and replenished water supplies, others may face drought conditions and water scarcity, impacting drinking water supplies, agriculture, and industry.
- Ecological Effects: La Nina can have profound ecological effects, including changes in vegetation patterns, wildlife habitats, and biodiversity. These impacts can reverberate throughout ecosystems, affecting species interactions, population dynamics, and ecosystem services.
- Global Climate Patterns: La Nina is part of the broader climate system and can interact with other climate phenomena, influencing global climate patterns such as the jet stream and atmospheric circulation. These interactions can have cascading effects on weather and climate across different regions of the world.
Impact on India:
In some regions of India, La Nina can bring above-average rainfall during the monsoon season. This increased precipitation can benefit agricultural productivity by providing ample water for crops, leading to higher yields and potentially boosting agricultural output.


Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.